Buying Guide for the Best pH Meters
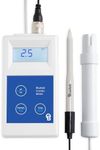
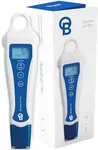
Choosing the right pH meter is important whether you're testing water for gardening, aquariums, pools, or laboratory work. The best pH meter for you depends on how often you'll use it, how accurate you need the readings to be, and the environment in which you'll use it. Understanding the key features will help you make a confident choice that matches your needs.AccuracyAccuracy tells you how close the pH meter's readings are to the true pH value. This is important because a small error can make a big difference, especially in scientific or sensitive applications. Accuracy is usually shown as ±0.1, ±0.01, or similar. For casual use like gardening or pools, ±0.1 is often enough. For laboratory or research work, look for ±0.01 or better. Think about how precise your measurements need to be and choose accordingly.
RangeThe range indicates the lowest and highest pH values the meter can measure, such as 0-14. Most pH meters cover the full 0-14 range, which is suitable for most uses. However, if you know your samples will always be within a certain range, you can focus on meters that are most accurate in that area. For general use, a full-range meter is usually the best choice.
CalibrationCalibration is the process of setting the meter to known standards to ensure accurate readings. Some meters require manual calibration, where you adjust the meter using calibration solutions, while others offer automatic calibration, making the process easier. If you want convenience and less hassle, look for automatic calibration. If you don't mind a bit of extra work and want more control, manual calibration can be fine. Regular calibration is important for all meters to maintain accuracy.
Display TypeThe display shows your pH readings. Some meters have simple digital screens, while others offer backlit or multi-line displays that show temperature and other information. If you'll be using the meter in low light or need to see extra data, a backlit or more advanced display can be helpful. For basic needs, a simple digital display is usually enough.
PortabilityPortability refers to how easy it is to carry and use the meter in different locations. Handheld or pen-style meters are lightweight and easy to use on the go, making them great for fieldwork or quick tests. Benchtop meters are larger and better for stationary use, like in a lab. Consider where you'll be using the meter most often to decide which style fits your needs.
WaterproofingWaterproofing protects the meter from damage if it gets wet. This is especially important if you'll be using the meter outdoors, near water, or in messy environments. Waterproof meters are more durable and reliable in these situations. If you only use the meter indoors and away from water, waterproofing may be less important.
Temperature CompensationTemperature compensation means the meter can adjust its readings based on the temperature of the liquid being tested, since pH readings can change with temperature. Some meters do this automatically (ATC), while others require manual adjustment. If you test samples at different temperatures, automatic temperature compensation is very useful. For consistent, room-temperature testing, this feature is less critical.
Electrode Type and ReplacementThe electrode is the part of the meter that actually senses the pH. Some meters have built-in electrodes, while others have replaceable ones. Replaceable electrodes are useful if you plan to use the meter often or in harsh conditions, as electrodes can wear out over time. Built-in electrodes are fine for occasional use. Think about how often you'll use the meter and whether you'll want to replace just the electrode or the whole meter when it wears out.